Artificial intelligence (AI) is no longer just a tool for automation—it is evolving into an autonomous decision-maker, capable of optimising processes, predicting outcomes, and adapting in real time.
As AI systems advance, businesses must distinguish between AI Agents and Agentic AI, two concepts shaping the future of intelligent automation.
This shift is especially significant in finance, where AI is no longer just assisting traders and analysts but actively optimising investments, managing risks, and shaping market strategies.
The development of AI agents can be categorised into five levels, progressing from reactive systems to adaptive, self-learning models.
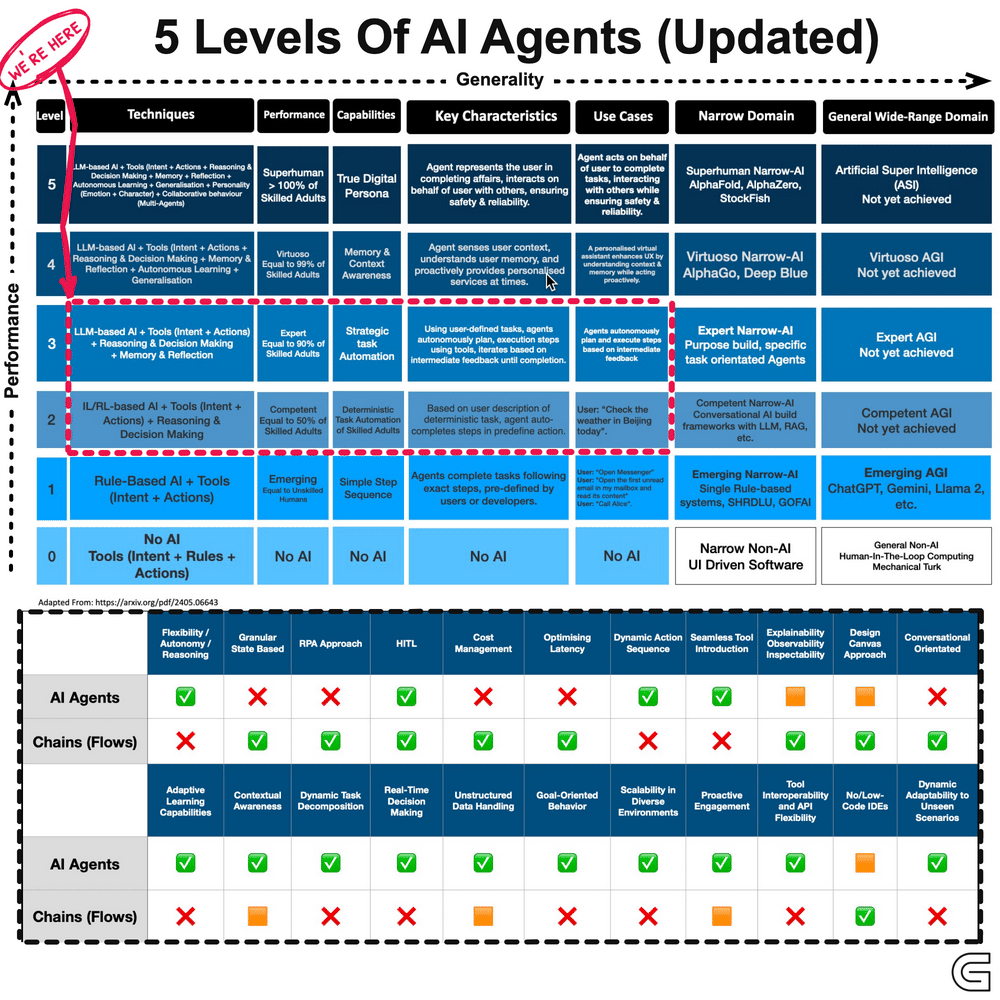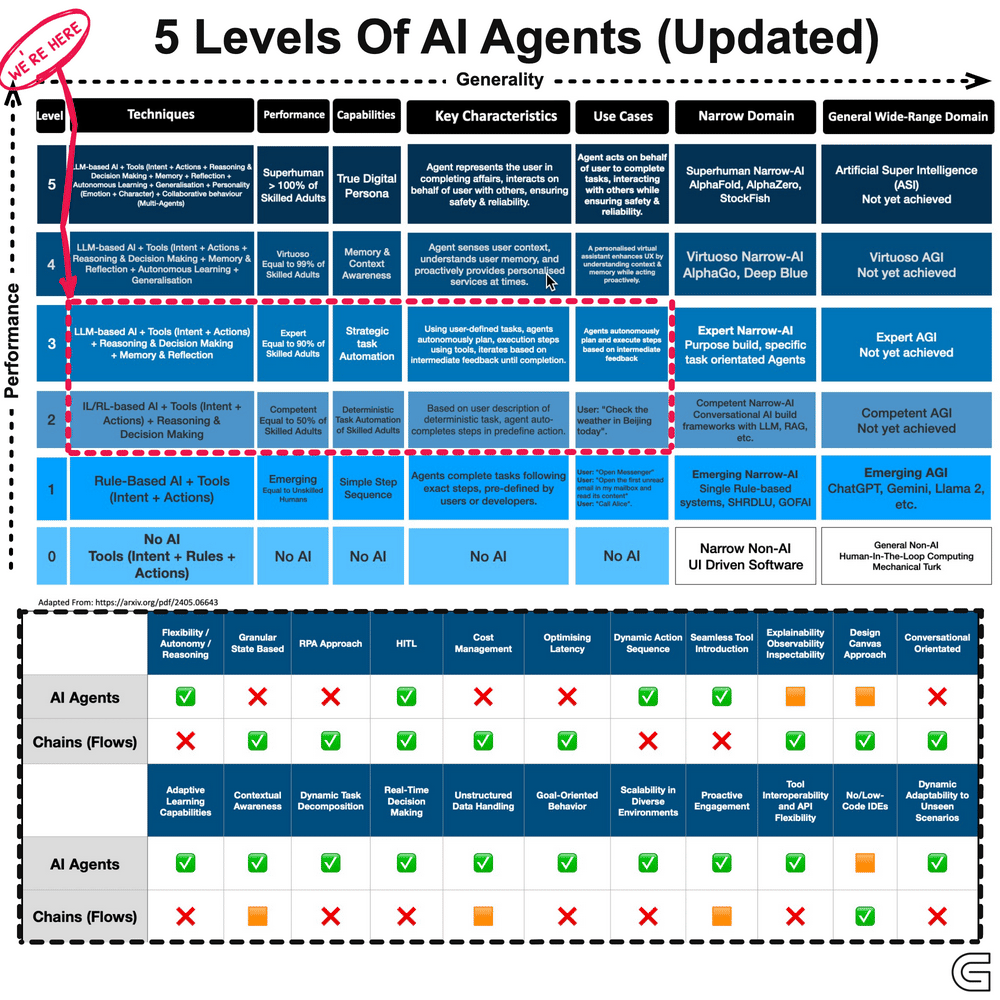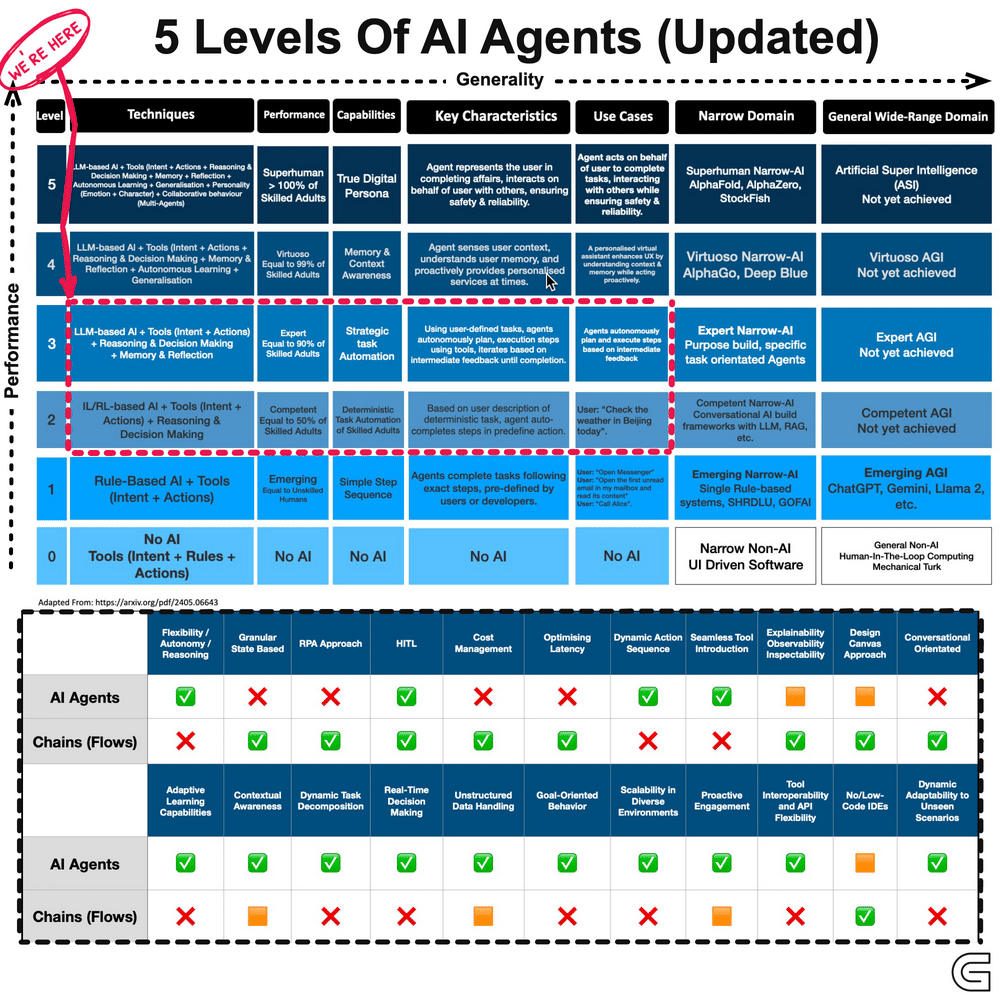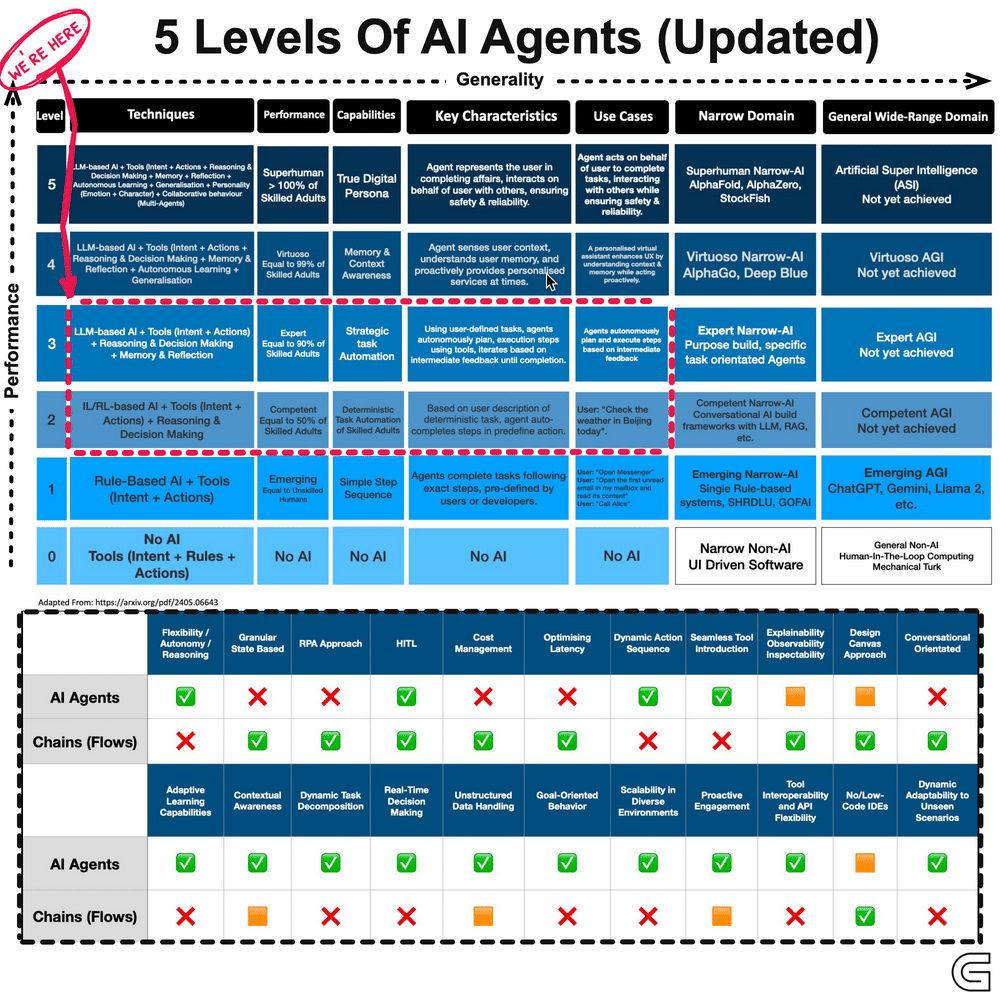
(GIF Source: https://cobusgreyling.medium.com/)
These agents function based on predefined rules and react to specific inputs without memory or learning capabilities. They execute tasks efficiently within a fixed scope but cannot adapt to new scenarios.
Examples include basic chatbots and automated customer support systems that operate based on scripted responses.
At this stage, AI agents build an internal model of their environment, allowing them to interpret context and respond more intelligently. While they remain rule-based, they are more flexible than reactive systems.
Voice assistants and rule-based recommendation engines operate within this category, offering structured but slightly adaptive interactions.
These agents go beyond reactive responses by working towards specific objectives. They assess multiple courses of action and determine the best path to achieve a desired outcome.
Self-driving cars that evaluate traffic conditions in real time to optimise routes are an example of this level of intelligence.
At this level, AI systems do not just follow goals but also optimise decisions by weighing different variables. Instead of executing a task in a predefined way, they determine the most effective approach based on available data.
AI-powered financial advisors, for instance, analyse market trends and user risk tolerance to provide optimised investment strategies.
This is the most advanced form of AI agents, capable of continuous learning and adaptation. These systems refine their strategies over time, improving their decision-making based on experience rather than static programming.
Personalised recommendation systems that evolve with user preferences and AI-driven operational automation that refines workflows fall under this category.
The financial sector has rapidly adopted AI, transitioning from automated data analysis to AI-driven decision-making. AI Agents are now integral to portfolio management, risk assessment, and high-frequency trading.
Each level of AI maturity corresponds to a shift in how financial institutions use AI to manage risk, investments, and strategy:
The progression from AI Agents to Agentic AI is particularly transformative for finance, where real-time adaptability is critical.
Financial institutions are leveraging AI Agents to:
However, Agentic AI represents the next evolution, where AI does not just execute tasks but actively shapes financial strategies—adjusting risk exposure, identifying emerging investment trends, and optimising asset allocation.
While AI agents operate within a set framework, agentic AI represents a new level of autonomy. It is characterised by goal-setting, strategic decision-making, and real-time adaptation, moving AI from being a reactive system to an independent actor in business operations.
| Feature | AI Agents | Agentic AI |
|---|---|---|
| Task Execution | Performs predefined tasks | Independently pursues complex objectives |
| Decision-Making | Follows rules, limited flexibility | Self-directed, adjusts actions dynamically |
| Learning Ability | Static, requires human updates | Continuously refines strategies based on new data |
| Adaptability | Operates within fixed conditions | Adjusts to changing environments in real time |
| Complexity Handling | Designed for specific tasks | Manages multi-step processes and problem-solving |
Agentic AI represents a shift from task-based automation to strategic intelligence. Unlike traditional AI agents that require structured workflows, agentic AI can independently:
In business environments, this translates into AI systems that not only automate tasks but also optimise operations proactively. Agentic AI can manage workflows, identify inefficiencies, and refine business strategies without constant reprogramming.
The transition from AI agents to agentic AI represents a significant evolution in artificial intelligence. Businesses that understand and embrace this shift will be better positioned to leverage AI for scalable, intelligent decision-making rather than just process automation.
For organisations exploring AI implementation, the key is aligning the level of intelligence required with business objectives. If automation is the priority, AI agents can handle structured workflows efficiently. If the goal is dynamic, self-improving AI, then agentic AI provides a competitive edge.
Our flagship platform – OneNexus, we provide AI-powered solutions that help businesses navigate this transformation. Whether enhancing operational efficiency, automating financial processes, or enabling AI-driven decision-making, we bridge the gap between automation and intelligence.
The future of AI is not just about executing commands—it is about AI taking an active role in shaping business outcomes. Companies that integrate more autonomous, adaptable AI systems will drive the next wave of innovation and efficiency in their industries.
📖 For further insights, refer to Cobus Greyling’s work on AI agent levels here.
#AI #ArtificialIntelligence #AgenticAI #Automation #Nexus #Innovation
Level 39, One Canada Square,
Canary Wharf, London
E14 5AB
6 Battery Rd, #03-62,
The Work Project @ Six Battery Road
Singapore 049909
Studio 1006, Dreamplex Thai Ha, 10th floor 174 Thai Ha Str, Dong Da Ward
Hanoi 100000, Vietnam
Otemachi Building 4th Floor
Otemachi 1-6-1, Chiyoda
Tokyo 100-0004, Japan